Is There A Downside To Having Solar?
Is There A Downside To Having Solar? Have you ever considered the possibility of harnessing the power of the sun to fuel your home? Solar energy has gained immense popularity in recent years due to its undeniable environmental benefits. However, amidst the hype and allure of going solar, it’s important to ask ourselves: is there a downside to having solar? While it may seem like a perfect energy solution, this article aims to explore the potential drawbacks of adopting solar energy and shed light on the realities that may come with this renewable energy source.
Cost of Installation
Initial Investment
Installing solar panels can be a significant investment, requiring a substantial initial cost. While the prices of solar panels have decreased in recent years, the overall cost of installation can still be a barrier for many individuals and businesses. However, it is important to consider the long-term benefits and potential savings on energy bills that solar panels can offer.
Solar panel systems generally require very little maintenance, which can be seen as a great advantage. However, occasional maintenance and repairs may still be necessary over the lifetime of the system. These costs should be factored into the overall financial calculations when considering the installation of solar panels. Regular cleaning of panels and ensuring proper functioning of inverters and other components are essential to ensure optimal performance.
Battery Storage Costs
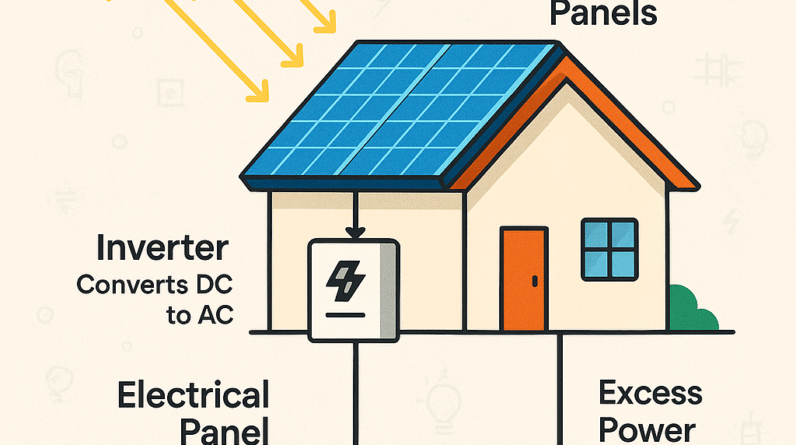
While solar energy allows for the generation of electricity during daylight hours, excess energy produced may need to be stored for use during nighttime or periods of low sunlight. Battery storage systems can provide a solution, but they add an additional cost to the installation. Depending on the energy demands of the household or business, the size and capacity of the battery storage system needed can greatly impact the overall cost.

Intermittent Power Generation
Dependency on Sunlight
Solar panels rely on sunlight to generate electricity. Therefore, their effectiveness is dependent on the availability of sunlight. Areas with limited sunlight or regions that experience frequent cloudy days may not be ideal for solar energy production. This intermittency can pose challenges and may require alternative energy sources to supplement solar power.
Seasonal Variations
The amount of sunlight available throughout the year can also vary significantly based on seasonal changes. In some regions, shorter days and lower angles of sunlight during winter months can result in reduced solar energy production. This seasonal variation should be considered when analyzing the feasibility and expected output of solar panel systems.
Naturally, solar panels are unable to generate electricity during nighttime hours and produce less energy on cloudy days. This can limit the reliability and consistency of solar power as the sole source of energy. However, many solar energy systems are connected to the power grid, allowing excess energy to be sold back to the grid and providing a reliable source of electricity during times when solar energy production is insufficient.
Limited Efficiency and Output
Size and Placement Limitations
Solar panels require ample space and proper placement to maximize their efficiency and output. In instances where space is limited, such as in urban areas or apartments, it may be challenging to install a sufficient number of panels to meet energy demands. Additionally, surrounding structures or shading from trees and buildings can impact the performance of solar panels, further reducing their output.
Losses in Conversion and Transmission
When converting sunlight into electricity, there are inevitable losses in the efficiency of the conversion process. This means that not all sunlight captured by solar panels is successfully converted into usable energy. Similarly, during transmission of electricity from the panels to the end user, losses can occur. These losses contribute to a reduction in the overall efficiency and output of solar energy systems.
Energy Storage Limitations
While advancements have been made in battery storage technology for solar energy systems, there are still limitations on the amount of energy that can be effectively stored. This can be a challenge when attempting to rely solely on solar power, as extended periods of low sunlight or increased energy demands may exceed the storage capacity of the system. Proper sizing and management of battery storage systems are crucial to overcome these limitations.
Environmental Impact

Production and Disposal of Solar Panels
Although solar energy is considered a clean source of power, the production of solar panels and their components does have an environmental impact. The manufacturing process requires energy and raw materials, and the disposal of panels at the end of their lifespan can pose challenges for proper recycling and waste management. Ensuring responsible manufacturing and recycling practices can mitigate some of these environmental concerns.
Land Use and Habitat Disruption
Solar farms require large amounts of land to accommodate a significant number of solar panels. This can result in the use of arable land or the disruption of natural habitats and ecosystems. It is important to carefully consider the location and design of solar farms to minimize their impact on local flora and fauna.
Water Consumption in Solar Farms
Some solar technologies, such as concentrated solar power, require water for cooling. In regions where water scarcity is a concern, this can be a significant drawback. Approaches that reduce water consumption or utilize alternative cooling methods can help address this issue and minimize the environmental impact of solar farms.
Reliability and Dependence
While solar energy systems can provide electricity directly to a property, many installations are connected to the power grid. This means that during periods of low sunlight or high energy demand, a property may still rely on the grid for electricity. The level of reliability and independence from the grid will depend on the size and capacity of the solar energy system and the energy demands of the property.
Failures and Outages
Like any electrical system, solar panels are not immune to failures or outages. Technical issues or damage to panels can result in reduced or even complete loss of energy production. It is important to consider the potential for failures and the availability of maintenance and repair services when weighing the benefits and drawbacks of solar energy.
Backup Power Considerations
In order to ensure a continuous power supply, backup power solutions may be necessary when relying on solar energy. This could include options such as generators or connecting to a backup power system provided by the grid. Determining the appropriate backup power solution and the associated costs should be considered when evaluating the overall reliability and dependence on solar energy.
Aesthetics and Property Value
Visual Impact
The installation of solar panels can alter the visual appearance of a property, which may be a concern for some individuals or communities. The panels themselves can be perceived as unsightly, especially if they are not properly integrated into the design of the building. However, advancements in solar panel design and aesthetic options are making it possible to minimize the visual impact of solar installations.
In some areas, there may be restrictions or regulations that limit the installation of solar panels. These restrictions could relate to historical preservation, homeowner’s association regulations, or local building codes. It is important to research and understand any such limitations before investing in solar energy systems.

Effect on Property Resale Value
While solar panels can increase the value of a property by providing a potential energy cost savings for future owners, there is also a possibility that some potential buyers may perceive them as a drawback. It is important to consider the potential impact on property resale value when deciding to install solar panels.
Challenges for Renters and Apartment Dwellers
Limited Control and Ownership
For renters and apartment dwellers, the installation of solar panels may not be feasible or even allowed due to the lack of control and ownership of the property. In such cases, individuals may need to explore alternative options, such as community solar programs or advocating for renewable energy initiatives in their communities.
Even for property owners, obtaining permission and necessary approvals for solar panel installation can be a challenge. Homeowner’s associations or local regulations may impose restrictions or require specific guidelines to be met. It is important to research and comply with these requirements to ensure a smooth and successful installation process.
Incentives and Programs
Renters and apartment dwellers may face additional challenges in accessing government incentives and programs that promote solar energy. Many incentives are targeted at property owners, and the lack of ownership can limit the financial benefits that can be obtained through these programs. However, some regions offer community solar initiatives that allow individuals to invest in shared solar farms and receive credits for the energy produced.
Geographical Suitability
Sunlight Availability
The amount of sunlight available varies depending on geographical location. Areas closer to the equator generally receive more sunlight throughout the year, making them more suitable for solar energy production. In contrast, regions that experience extended periods of cloud cover or limited daylight hours may not be as conducive to solar power generation.
Climate and Weather Conditions
Extreme weather conditions, such as heavy snowfall or frequent hailstorms, can pose challenges for solar panels. Accumulated snow or damage from hail can reduce the efficiency of the panels and require additional maintenance and repairs. Understanding the climate and weather patterns of a region is important when considering the installation of solar panels.
Contradictions in Urban Areas
While solar energy can potentially be harnessed in urban areas, there are specific challenges related to available space and infrastructure. The presence of tall buildings and limited roof space can make it difficult to install solar panels. However, innovative solutions such as solar installations on vertical surfaces or integration with urban infrastructure are being explored to overcome these challenges.
Social and Economic Equity
Initial Affordability
The upfront cost of solar panel installation can pose a barrier to affordability for some individuals or communities. Lower-income households may find it challenging to access the financial resources required for installation, limiting their ability to take advantage of the benefits of solar energy. Initiatives aimed at promoting affordability and access to solar energy for all socioeconomic groups can help address this issue.
Access to Government Incentives
Government incentives and subsidies for solar energy can significantly impact the affordability and accessibility of solar panels. Unfortunately, not all individuals and communities have equal access to these incentives. Ensuring that government programs are inclusive and accessible to all socioeconomic groups is crucial to promoting social and economic equity in the adoption of solar energy.
Socio-economic Disparities
The availability of solar energy and the ability to harness its benefits can further deepen existing socio-economic disparities. Communities that are already marginalized may face additional challenges in accessing the benefits of solar energy due to lack of resources, limited exposure to information, or systemic barriers. Efforts should be made to bridge these disparities and ensure equitable distribution of solar energy resources.
Impact on Energy Grid
As the adoption of solar energy grows, the integration of these systems into the existing energy grid can present challenges. The intermittent nature of solar power generation and the need to balance supply and demand on the grid require careful planning and coordination. Upgrading and modernizing the energy grid to accommodate the increasing use of solar energy is essential for its efficient and effective operation.
Transmission and Distribution Upgrades
The decentralized nature of solar energy production necessitates upgrades to transmission and distribution infrastructure. Ensuring that the grid is capable of handling the influx of electricity produced by solar panels and delivering it to end users without significant losses or disruptions is crucial. These upgrades can be costly and require ongoing maintenance to keep pace with the increasing demand for solar power.
Grid Stability and Balancing
The intermittent nature of solar energy production can pose challenges to grid stability and balancing. As the availability of solar power fluctuates throughout the day, mechanisms must be in place to balance the supply and demand of electricity. Energy storage, smart grid technologies, and demand response programs are among the solutions being explored to address these challenges and maintain grid stability.