How Many Solar Panels Does It Take To Run A House Off The Grid?
How Many Solar Panels Does It Take To Run A House Off The Grid? Imagine the freedom and self-sufficiency of living off the grid, powering your home solely with the abundant energy of the sun. But how many solar panels would you actually need to make this dream a reality? In this article, we will explore the answer to this burning question and provide you with valuable insights on the number of solar panels required to run a house off the grid. Say goodbye to electricity bills, and let’s embark on this fascinating journey towards a more sustainable and independent lifestyle.
Calculating Energy Consumption
Determining energy needs
To determine the energy needs of your household, you must first assess your daily usage. Take into account all the electrical appliances and devices you use on a regular basis, as well as their power requirements, measured in watts. Consider appliances such as refrigerators, air conditioners, televisions, washing machines, and lights. Make a list of these items and note down their power ratings.
Once you have a comprehensive list, multiply the power rating (in watts) of each appliance by the approximate number of hours you use it in a day. This will give you the energy consumption of each appliance in watt-hours (Wh) per day. Add up these values to determine your daily energy usage.
Calculating daily energy usage
To calculate your daily energy usage, you need to add up the energy consumption of all the appliances and devices in your household. For example, if you have a refrigerator that uses 150 watts and runs for 8 hours a day, it will consume 1,200 watt-hours (Wh) of energy. Repeat this calculation for each appliance and device, and then sum up the total energy consumption.
Keep in mind that some appliances have different power ratings depending on their settings or modes of operation. For instance, an air conditioner may consume more energy when set to a lower temperature. It’s important to take these variations into account to get an accurate estimate of your daily energy usage.
Typical Solar Panel Output
Understanding solar panel efficiency
Solar panel efficiency refers to the ability of a solar panel to convert sunlight into usable electricity. Higher efficiency panels can generate more electricity for a given amount of sunlight. The efficiency of solar panels is usually expressed as a percentage, representing the amount of sunlight they can convert into electricity.
Most commercially available solar panels have an efficiency ranging from 15% to 20%, although some premium panels can exceed 20%. When selecting solar panels for your system, it’s important to consider their efficiency to ensure you get the maximum output from the available sunlight.
Factors affecting panel output
Several factors can affect the output of solar panels. One of the most significant factors is sunlight intensity, which varies throughout the day and throughout the year. Panels will generate more electricity during peak sunlight hours compared to early mornings or late afternoons.
Other factors that can impact panel output include shading, dirt or dust buildup on the panels, temperature, and the angle at which they are installed. It’s important to choose a suitable location for the panels and regularly maintain them to maximize their output.
Sizing the Solar Panel System
Determining system capacity
To size your solar panel system, you need to consider your energy needs and the solar panel output. Calculate the average daily energy consumption of your household and then divide it by the daily output of a single solar panel. This will give you an estimate of how many panels you need.
For example, if your daily energy consumption is 10,000 watt-hours (Wh) and a single solar panel has an output of 250 Wh, you would need approximately 40 solar panels to meet your energy needs.
In addition to sizing the solar panel system, you may also want to consider incorporating battery storage into your setup. Batteries can store excess energy generated by the panels during the day and provide electricity during the night or when sunlight is limited. They also serve as a backup power source during grid outages.
When sizing your battery storage, calculate the amount of energy you need to store for your nighttime usage or during periods of low sunlight. Consider the capacity of the batteries and their efficiency in storing and discharging energy.
Location and Sunlight Availability
Evaluating the sun exposure
Before installing solar panels, it’s crucial to evaluate the amount of sunlight your location receives. Generally, areas with more sunlight will yield higher energy output from solar panels. Consider potential shading from nearby buildings, trees, or other obstructions that may reduce the amount of sunlight reaching your panels.
Determine the ideal location on your property that receives the most sunlight throughout the day. South-facing rooftops or open areas without significant shading are typically the best options for solar panel installation.

Accounting for weather conditions
While sunlight is the primary source of energy for solar panels, weather conditions can impact their output. Cloudy or overcast days may reduce the amount of sunlight reaching the panels, resulting in lower energy generation. However, modern solar panels are still capable of producing electricity even under cloudy conditions.
It’s important to factor in regional weather patterns and consider the average number of sunny days per year when evaluating the feasibility of a solar panel system. Assess the overall climate of your location to ensure that the solar panels will provide sufficient energy throughout the year.
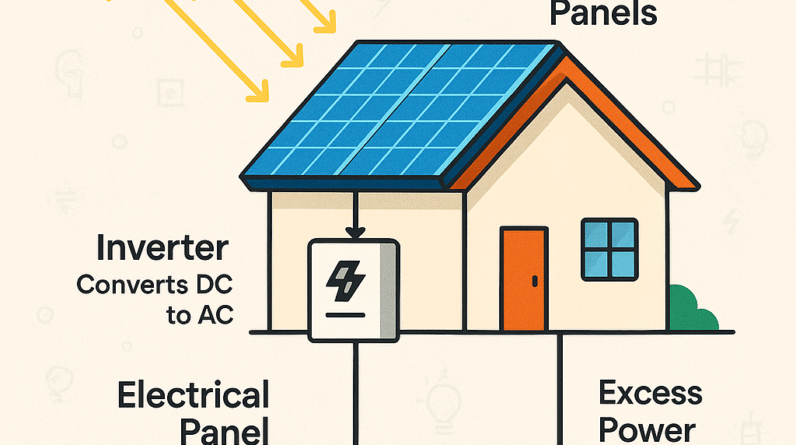
Using inverters and charge controllers
Solar panels produce direct current (DC) electricity, which needs to be converted into alternating current (AC) for household use. This is where inverters come into play. Inverters convert the DC electricity generated by solar panels into AC electricity that can be used to power your appliances.
Additionally, charge controllers regulate the charging and discharging of batteries in a solar panel system. They ensure that the batteries are charged efficiently and protect them from overcharging or discharging too much.
Choosing battery capacity
When incorporating battery storage into your solar panel system, it’s crucial to consider the capacity of the batteries. The battery capacity should be sufficient to store excess energy generated during the day and meet your energy needs during periods of low sunlight or at night. Calculate the energy consumption during these periods and select batteries with an appropriate capacity.
Consider the depth of discharge (DoD) rating of the batteries, which represents the percentage of their total capacity that can be safely used before recharging. It’s important to avoid deep discharges to prolong battery life and ensure optimal performance.
Efficiency and Load Management
Implementing energy-efficient practices
To maximize the efficiency of your solar panel system, implement energy-efficient practices in your household. This includes using energy-saving appliances, such as LED lights and energy-efficient refrigerators. Additionally, minimize standby power consumption by unplugging electronics when not in use.
Another energy-saving technique is to use natural lighting during the day instead of relying on electrical lights. Take advantage of daylight and position windows strategically to bring in sunlight and reduce the need for artificial lighting.
Monitoring and managing power usage
To better understand and manage your power usage, consider installing a monitoring system that tracks the energy output and consumption of your solar panel system in real-time. This can provide valuable insights into your energy usage patterns and help you identify areas where you can further optimize energy consumption.
By actively monitoring and managing your power usage, you can make more informed decisions, optimize the performance of your solar panel system, and potentially reduce your overall energy costs.
Backup Power or Grid-Tied System
Determining the need for backup power
Decide whether you require a backup power source in case of grid outages. If your area experiences frequent power outages or if you prioritize having uninterrupted power supply, you may consider incorporating a backup power system into your solar panel setup. This can involve the use of batteries or backup generators.
Exploring grid-tied options
Alternatively, you can opt for a grid-tied solar panel system. With this setup, your solar panels are connected to the electrical grid. Any excess energy generated by the panels can be fed back into the grid, earning you credits or compensation from the utility company. This reduces the need for battery storage and provides a seamless transition between solar power and grid power.
Grid-tied systems are advantageous if your area has a reliable grid and offers favorable net metering policies. However, during grid outages, a grid-tied system may not be able to provide power to your home unless you have backup power sources.
Selecting the right solar panel system
When choosing a solar panel system, consider factors such as the quality and reliability of the panels, the reputation of the manufacturer, and the warranty offered. Look for certified and tested panels that meet industry standards for efficiency and durability.
Additionally, evaluate the installation requirements and compatibility of the system with your property. Consider your roof’s condition, orientation, and structural integrity, as well as any local regulations or permits required for installation.
Hiring a professional installer
While it is possible to install solar panels on your own, hiring a professional installer is highly recommended. Experienced installers have the necessary expertise to assess your energy needs, design an optimal system, and ensure safe and efficient installation. They can also handle any necessary paperwork and permits, saving you time and effort.
Research local solar panel installers, read customer reviews, and get multiple quotes to find a reputable and qualified installer who can ensure a smooth and successful installation process.
Return on Investment
Calculating payback period
Investing in a solar panel system involves upfront costs, but it can lead to long-term financial benefits. To determine the return on investment (ROI) of your solar panels, calculate the payback period. The payback period represents the time it takes for the energy savings generated by the solar panels to surpass the initial investment cost.
To calculate the payback period, divide the total cost of the solar panel system by the annual energy savings. This will give you the number of years it will take to recoup your investment through energy savings. Keep in mind that the payback period can vary depending on factors such as the cost of electricity in your area, government incentives, and the longevity of the solar panel system.

Considering financial incentives
When evaluating the financial aspects of installing solar panels, explore any available financial incentives offered by the government or local utility companies. These incentives can include tax credits, grants, rebates, or feed-in tariffs. Such incentives can significantly reduce the upfront costs and shorten the payback period, making solar panel installation more financially viable.
Research regional or national incentive programs and consult with a solar panel professional to understand and take advantage of any available financial incentives.
Performing regular maintenance
To ensure the long-term performance and longevity of your solar panel system, regular maintenance is essential. Cleaning the panels regularly to remove dust, dirt, or debris build-up is crucial, as it can significantly impact their efficiency. Inspect the panels for any cracks, loose connections, or damage, and promptly address any issues.
Additionally, trim or remove any foliage that may shade the panels to maintain optimal sunlight exposure. Consult the manufacturer’s guidelines or seek professional advice on specific maintenance procedures and schedules for your solar panel system.
Understanding solar panel lifespan
Solar panels are designed to withstand various environmental conditions and have a typical lifespan of 25 to 30 years or more. However, their efficiency may slightly decrease over time. It’s important to consider the expected lifespan of the panels when calculating the return on investment and evaluating the long-term benefits of solar panel installation.
Regular maintenance and monitoring will help ensure that your solar panel system continues to operate at its optimal performance level throughout its lifespan. Stay proactive in addressing any issues and follow the recommended maintenance guidelines to maximize the longevity of your solar panels.