How Many Solar Panels Does It Take To Power A House?
How Many Solar Panels Does It Take To Power A House? Imagine never having to worry about your electricity bill again. With the rising costs of energy, more and more homeowners are turning to solar power as a sustainable and cost-effective solution. But how many solar panels does it take to power a house? In this article, we will explore the factors that determine the number of solar panels needed, including the size of your home, energy consumption, and geographical location. So, whether you are considering going solar or simply curious about the potential of solar power, keep reading to find out the answer to this burning question.
Understanding Solar Panel Basics
Solar Panel Efficiency
When considering solar panel systems for your home, one of the key factors to understand is solar panel efficiency. Solar panel efficiency refers to how effectively the panel converts sunlight into usable electricity. Higher efficiency panels produce more electricity, which means you can generate more power from a smaller area of panels. The efficiency of solar panels can vary depending on the technology used, with monocrystalline panels generally being more efficient than polycrystalline panels. Understanding the efficiency of solar panels is important when determining the size and capacity of your solar panel system.

Solar Panel Size
Solar panel size refers to the physical dimensions of the panels themselves. The size of solar panels can vary, with common residential panels ranging from 60 to 72 cells. The size of the solar panels will affect the overall capacity and output of your solar panel system. Larger panels can generate more electricity, but they may also require more space for installation. When considering solar panel size, it’s essential to assess the available roof space and consider how many panels can be accommodated.
Solar Panel Output
Solar panel output refers to the amount of electricity that a panel can produce under optimal conditions. The output is measured in watts and indicates the capacity of a panel to generate power. The output of a solar panel depends on various factors, such as the size and efficiency of the panel, as well as external factors like sunlight intensity and temperature. Understanding the potential output of your solar panels will help you determine the number of panels needed to meet your energy demand.
Calculating Energy Demand
Average Household Energy Consumption
Before determining the capacity of your solar panel system, it’s important to understand your household’s energy consumption. The average household energy consumption varies depending on factors such as the number of occupants and their energy usage habits. To calculate your energy demand, you can review your utility bills or use online calculators that estimate energy usage based on different appliances and activities. By understanding your energy consumption, you can have a clearer idea of how much solar energy you need to generate to meet your needs.
Factors Affecting Energy Demand
Several factors can influence your overall energy demand. These factors include the size of your home, the number of occupants, the types of appliances used, and lifestyle choices. For example, a large family with multiple televisions and air conditioning units will typically have higher energy demand compared to a smaller household with more energy-efficient appliances. When determining your energy demand, it’s important to consider these factors to ensure your solar panel system can meet your specific needs.
Determining Solar Panel Capacity
Solar Panel Capacity Calculation
Once you have a clear understanding of your energy demand, you can calculate the capacity of your solar panel system. Solar panel capacity is measured in kilowatts (kW) and represents the amount of power the system can generate under optimal conditions. To calculate the solar panel capacity needed, divide your average daily energy consumption in kilowatt-hours (kWh) by the average daily peak sunlight hours in your location. This calculation will give you an estimate of the capacity required for your solar panel system.

Location-based Considerations
The location of your home plays a vital role in determining the capacity of your solar panel system. Different regions receive varying amounts of sunlight throughout the year. Areas with more sunlight will generally require less solar panel capacity to meet energy demand, while regions with lower sunlight levels may need a larger solar panel capacity. It is crucial to take into account the average sunlight hours in your location to ensure your system can generate sufficient electricity throughout the year.
Storage and Backup Power
When determining solar panel capacity, it’s also important to consider storage and backup power options. Solar panels generate electricity during the daytime when the sun is shining. If you are unable to use all the electricity generated or want to have a backup power supply during periods of low sunlight or power outages, you may need to incorporate a battery storage system. Battery storage allows you to store excess energy produced by your solar panels and use it when needed. Adding storage capacity to your solar panel system will ensure a reliable power supply even when sunlight conditions are unfavorable.
Types of Solar Panel Systems
Grid-tied System
A grid-tied solar panel system is the most common type of residential installation. With this system, your solar panels are connected to the main electrical grid. When your solar panels produce more electricity than your home needs, the excess power is sent back to the grid, and you receive credits or compensation from your utility company. During times when your energy demand exceeds the output of your solar panels, you can draw power from the grid. Grid-tied systems are cost-effective and allow you to benefit from net metering programs offered by utility companies.
Off-grid System
An off-grid solar panel system is typically used in remote areas where there is no access to the electrical grid. With an off-grid system, your solar panels generate electricity that is stored in batteries for use during periods of low sunlight or at night. Off-grid systems require careful consideration of energy demand, battery capacity, and backup power options to ensure a reliable power supply. These systems provide independence from the grid but may require larger solar panel capacity and battery storage to meet your energy needs.
Hybrid System
A hybrid solar panel system combines elements of both grid-tied and off-grid systems. These systems are connected to the electrical grid but also incorporate battery storage. The batteries can store excess energy produced by the solar panels, which can be used during peak demand times or in the event of a power outage. Hybrid systems offer the benefits of both grid-tied and off-grid systems, providing a reliable power supply and potential savings through net metering.
Factors Influencing Solar Panel Installation
The available roof space is a crucial factor when considering solar panel installation. Solar panels require adequate space for installation to maximize sunlight exposure. The size of your roof and the presence of any obstructions, such as chimneys or vents, can impact the number of panels that can be installed. It’s important to assess the available roof space before determining the size and capacity of your solar panel system. This will ensure that you can install enough panels to meet your energy demand efficiently.
Orientation and Tilt of the Roof
The orientation and tilt of your roof also play a significant role in the effectiveness of your solar panel system. Ideally, solar panels should face south to capture the most sunlight throughout the day. However, east and west-facing orientations can still provide significant energy generation. The tilt of your roof should be optimized to maximize sunlight exposure. In some cases, a solar panel mounting system can be used to achieve the ideal tilt angle, ensuring optimal performance of your solar panel system.
Local Climate and Sunlight Exposure
The local climate and sunlight exposure in your area are essential considerations for solar panel installation. Areas with high levels of sunlight exposure will generally produce more electricity and require smaller solar panel capacities. Conversely, regions with lower sunlight levels may need larger solar panel capacities to meet energy demands. Understanding the climate and sunlight exposure in your location will help determine the appropriate size and capacity of your solar panel system to ensure optimal energy generation.
Energy Offset Percentage
Sizing a solar panel system involves determining the energy offset percentage, which refers to the portion of your energy demand that will be met by the solar panel system. The energy offset percentage depends on various factors, including available roof space, solar panel capacity, and available sunlight. Higher energy offset percentages indicate that a larger portion of your energy demands can be met by the solar panel system. It’s important to consider your energy offset goals to size your solar panel system accordingly.
System Sizing Equation
To calculate the size of your solar panel system, use the following equation:
System Size (kW) = Average Daily Energy Consumption (kWh) / Average Daily Peak Sunlight Hours
This equation takes into account your average daily energy consumption and the peak sunlight hours in your location. The result will give you the estimated capacity of your solar panel system in kilowatts (kW). It’s important to note that this is a rough estimate, and additional factors such as shading and temperature can affect the actual output of your solar panel system.
Battery Storage Considerations
If you are considering incorporating battery storage into your solar panel system, it’s important to factor in the storage capacity when sizing your system. Battery storage allows you to store excess energy produced by your solar panels for use during low sunlight or power outages. The size of the battery storage system depends on your energy storage needs and should be accounted for when determining the overall system size. By considering battery storage from the beginning, you can ensure your solar panel system adequately meets your energy demand.
Common Solar Panel Sizes and Capacities
Standard Solar Panel Sizes
Standard solar panels come in various sizes, typically ranging from 60 to 72 cells. These sizes correspond to the physical dimensions and electrical output of the panels. The most common panel sizes for residential installations are around 65 to 70 inches in height and 39 to 42 inches in width. The size of the solar panels will impact not only the physical space required for installation but also their capacity to generate electricity. Larger panels generally have higher capacity ratings and can generate more power.
Typical Solar Panel Capacity
Solar panel capacity refers to the amount of power a panel can produce under optimal conditions. The capacity of a standard solar panel can range from 250 to 400 watts. Higher capacity panels are typically more efficient and produce more electricity from the same amount of sunlight. When determining the capacity of your solar panel system, consider the average capacity of the panels you plan to use. This will help you estimate the number of panels needed to meet your energy demand efficiently.
Factors Affecting Solar Panel Output
Temperature
Temperature can impact the output of solar panels. High temperatures can lead to a decrease in the efficiency of panels and reduce their overall output. It’s essential to consider the average temperatures in your area when determining the capacity of your solar panel system. Additionally, proper ventilation and spacing between panels can help mitigate the negative effects of high temperatures and ensure optimal performance.
Shading
Shading is another factor that can significantly impact solar panel output. Even partial shading on a solar panel can significantly reduce its efficiency and overall energy generation. When assessing your roof for solar panel installation, consider any potential shading sources, such as nearby buildings, trees, or chimneys. Minimizing shading is crucial to maximize the output of your solar panel system and ensure efficient energy generation.
Accumulation of dirt and dust on solar panels can also affect their output. A layer of dirt or debris can block sunlight from reaching the solar cells and decrease the efficiency of the panels. Regular cleaning and maintenance of your solar panels are essential to ensure optimal performance. By keeping your panels clean, you can maximize their output and ensure efficient energy generation.

Other Considerations for Solar Panel Installation
Inverter Capacity
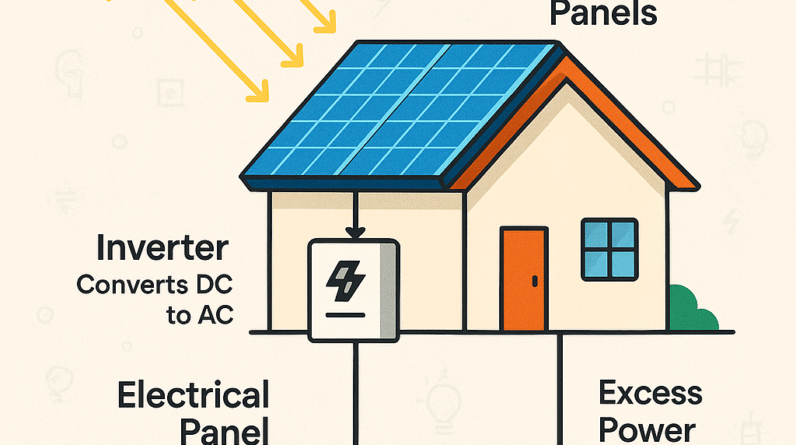
Inverter capacity is an important consideration when installing a solar panel system. The inverter converts the DC (direct current) electricity generated by the solar panels into AC (alternating current) electricity that can be used in your home or sent to the grid. The capacity of the inverter should match or exceed the capacity of your solar panel system to ensure efficient power conversion. It’s important to consult with a professional installer to determine the appropriate inverter capacity for your specific system.
Cost and Budget
The cost of installing solar panels and the budget available for the project is a significant consideration for many homeowners. The cost of solar panel systems can vary depending on factors such as panel size, capacity, and installation requirements. It’s important to research and obtain quotes from reputable installers to understand the costs involved. Additionally, consider potential incentives, rebates, and financing options that may be available to help offset the initial investment and make solar panel installation more affordable.
Permitting and Installation Process
Before installing solar panels, it’s important to understand the permitting and installation process in your area. Different regions may have specific requirements and regulations for solar panel installation. This can include obtaining permits, ensuring compliance with building codes, and coordinating with utility companies. Understanding the process and any associated timelines will help ensure a smooth installation and avoid any potential delays or issues.
Conclusion
Understanding the basics of solar panel systems is essential when considering installation for your home. By considering factors such as solar panel efficiency, size, and output, as well as your energy demand and location-specific considerations, you can determine the appropriate capacity and type of solar panel system for your needs. Factors such as available roof space, orientation, and tilt, as well as climate and shading, will influence the installation process and overall effectiveness of your solar panel system. By carefully assessing these factors and considering other considerations such as inverter capacity, cost, and permitting, you can make informed decisions and maximize the benefits of solar panel installation for your home.