Can You Run A House Completely On Solar Power?
Can You Run A House Completely On Solar Power? Imagine never having to worry about your electricity bill again. Picture a home where the power comes from the endless energy of the sun, potentially saving you thousands of dollars each year. We all know that solar power is environmentally friendly, but can it truly sustain a household’s energy needs entirely? In this article, we will explore the possibilities and limitations of running a house completely on solar power. Get ready to discover the remarkable advancements in solar technology and find out if it’s time for you to embrace a green and self-sufficient lifestyle.
Advantages of Solar Power for Homes
Reduced Energy Costs
One of the significant advantages of utilizing solar power for your home is the potential for reduced energy costs. Once you have installed a solar power system, you can generate your electricity, which means you won’t have to rely as heavily on traditional energy sources. This decreased reliance on the grid can result in significant savings on your monthly energy bills.
Solar power systems have the ability to produce more electricity during the day when the sun is at its peak, allowing you to rely less on electricity from the grid during these periods. Moreover, if your solar panels generate more energy than your household consumes, you may even be able to sell the excess energy back to the grid and receive credit or a monetary reimbursement for it.
In addition to saving on energy costs, solar power for homes offers notable environmental benefits. Solar energy is a clean and renewable source of power that produces no greenhouse gas emissions or air pollution. By harnessing the power of the sun, you can significantly reduce your carbon footprint and contribute to a greener and more sustainable future.
Switching to solar power also helps to mitigate the extraction and burning of fossil fuels, which are major contributors to climate change. By embracing solar energy, you are making a positive impact on the environment and helping to combat the pressing issue of global warming.
Energy Independence
Another advantage of having a solar power system for your home is the increased energy independence it provides. When you rely solely on the grid for your electricity needs, you are subjected to potential power outages and the fluctuations in energy prices determined by utility companies. However, by generating your own electricity through solar power, you become less dependent on external factors, such as grid failures or rising energy costs.
Solar power systems equipped with battery storage allow you to store excess energy generated during the day for use during periods of low sunlight or at night. This ensures a continuous power supply, even during blackouts or times of high demand. Solar power offers you the freedom to be in control of your energy production, providing a sense of security and independence.
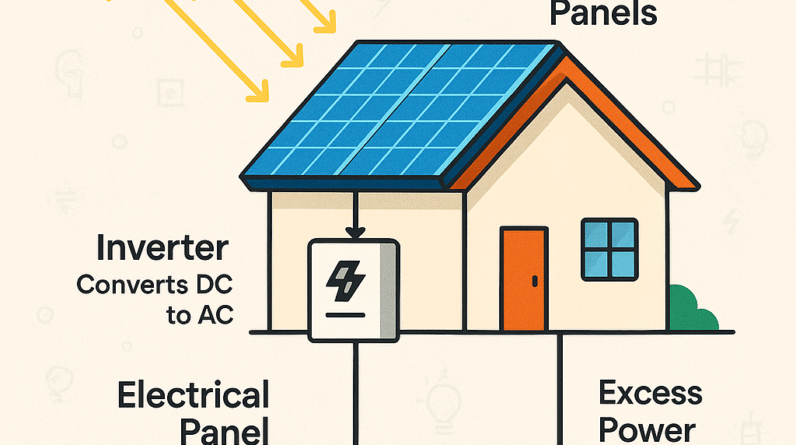
Components of a Solar Power System
The heart of any solar power system is the solar panels themselves. These panels, typically made of photovoltaic (PV) cells, convert sunlight into electricity. When sunlight strikes the PV cells, the photons in the light generate a flow of electrons, creating an electric current. The electrical energy generated by the solar panels can then be used to power your home or stored for later use.
Solar panels come in various sizes and types, including monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin film. The choice of solar panels depends on factors such as efficiency, cost, available space, and personal preferences. It is essential to consider these factors when selecting the most appropriate solar panels for your specific needs.
Inverter
The solar energy generated by the panels is in the form of direct current (DC), which needs to be converted into alternating current (AC) before it can be used by household appliances and electronics. This is where an inverter comes into play. The inverter converts the DC electricity produced by the solar panels into AC electricity that matches the voltage and frequency required by your home’s electrical system.
Inverters are available in different types, including string inverters, microinverters, and power optimizers. String inverters are usually the most cost-effective option for small to medium-sized solar power systems. Microinverters and power optimizers, on the other hand, offer advantages such as individual panel-level monitoring and increased efficiency.
Battery Storage
For homeowners seeking greater energy independence, investing in battery storage is a wise choice. Battery storage systems complement solar power by storing excess energy produced during the day for use during times when sunlight is limited, such as at night or during cloudy periods. By storing surplus energy, you are no longer solely reliant on the immediate availability of sunlight for your electricity needs.
Battery storage systems are typically connected to your solar panels and inverter. They store excess energy in the form of chemical energy, which can be converted back into electrical energy when needed. With the advancement of technology, battery storage systems have become more efficient, affordable, and compact, making them an increasingly popular addition to solar power systems.
Charge Controller
If you opt for a solar power system with battery storage, a charge controller becomes an integral component. The charge controller regulates the flow of electricity between the solar panels and the batteries, ensuring that the batteries are charged effectively and protected from overcharging and damage. It prevents excessive energy from being sent to the batteries when they are already fully charged, maintaining their longevity and performance.
A charge controller also plays a crucial role in preventing the batteries from discharging too much, which could diminish their overall capacity. By effectively managing the energy flow, the charge controller maximizes the efficiency and lifespan of your solar power system.

This image is property of images.unsplash.com.
Solar Panel Installation and Placement
Determining Solar Potential
Before installing a solar power system for your home, it is essential to evaluate the solar potential of your property. Factors such as the angle and orientation of your roof, shading from nearby structures or trees, and the geographical location of your home can impact the efficiency and productivity of your solar panels.
To determine your solar potential, consider hiring a professional solar installer or conducting a self-assessment by using online tools or solar calculators. These resources will take into account various factors to estimate your property’s solar potential and provide you with valuable insights into the energy production you can expect from solar panels.
Choosing the Right Installation Method
Solar panels can be installed using different mounting systems, each catered to specific requirements and conditions. The most common installation methods include roof-mounted and ground-mounted systems.
Roof-mounted systems are the preferred choice for many homeowners due to space limitations or aesthetic considerations. These systems involve installing the solar panels directly onto the existing roof structure. Ground-mounted systems, on the other hand, are installed on the ground using racks or poles. They offer more flexibility in terms of placement and can be tilted and adjusted to optimize solar exposure.
When selecting the installation method, consider factors such as available space, roof condition, local regulations, and personal preferences. Consulting with a professional installer can provide valuable guidance in choosing the most suitable installation method for your specific circumstances.
Optimal Placement for Maximum Efficiency
To ensure maximum efficiency and energy production, solar panels should be strategically placed to receive the most sunlight possible throughout the day. The tilt or angle of the panels and their orientation relative to the sun are critical factors in achieving optimal placement.
The optimal tilt angle for solar panels varies depending on the geographical location. A general rule of thumb is to set the tilt angle equal to the latitude of your location. However, slight adjustments may be necessary based on seasonal variations and specific local conditions.
In terms of orientation, solar panels typically perform best when facing south in the Northern Hemisphere or north in the Southern Hemisphere. This position maximizes the exposure to sunlight throughout the day, taking into account the sun’s path and the Earth’s tilt.
Professional solar installers can provide expert advice on the best placement options for your solar panels, ensuring you maximize the energy-generating potential of your system.
Sizing a Solar Power System
Calculating Energy Requirements
To determine the appropriate size of your solar power system, you need to assess your energy requirements. Analyze your household’s historical electricity consumption, considering factors such as seasonal variations and changes in energy use patterns. By understanding your energy needs, you can design a solar power system that caters specifically to your consumption.
Many electronic devices and appliances have wattage labels, indicating the amount of power they consume when in use. By summing up the power ratings of your devices and multiplying them by the average daily usage time, you can estimate your energy consumption. This calculation will give you a rough idea of the size of the solar power system needed to meet your energy requirements.
Determining Panel Capacity and Battery Storage
Once you have calculated your energy requirements, you can determine the appropriate panel capacity and battery storage for your solar power system. The panel capacity refers to the total energy output of your solar panels under specific conditions, typically measured in kilowatts (kW) or kilowatt-hours (kWh).
Consider the peak energy demand of your household, which usually occurs during the day when electricity usage is high, and sunlight is abundant. To size the panel capacity appropriately, ensure it can meet your peak demand while still generating excess energy to charge your battery storage system.
The battery storage capacity should be determined based on your desired level of energy independence and the amount of surplus energy you wish to store. Assessing your energy usage patterns will help you decide how much battery storage is necessary to fulfill your needs during periods of low sunlight or at night.
Consulting with a reputable solar installer or energy professional can help you accurately determine the panel capacity and battery storage required for your solar power system.
Considering Future Energy Needs
When sizing a solar power system, it is prudent to consider future energy needs alongside your current requirements. As your household grows or your energy consumption habits change, your energy needs may increase over time. Planning for potential future expansions or changes in energy demands allows you to design a solar power system that remains suitable and efficient in the long run.
By factoring in future energy needs, you can avoid the hassle and cost of upgrading your solar power system prematurely. Consider whether you are planning to add new appliances, expand your living space, or introduce electric vehicles into your household. Taking these future developments into account will help you size your solar power system appropriately from the beginning.

This image is property of images.unsplash.com.
Costs and Savings of Solar Power
Although solar power for homes offers substantial long-term savings, there are upfront costs associated with installing a solar power system. The total cost of a solar power system depends on factors such as the size of the system, the quality of components used, and the complexity of the installation.
Solar panels, inverters, battery storage, and charge controllers all contribute to the overall cost. Additionally, the cost of installation, including labor, permits, and wiring, should also be considered.
While upfront costs can initially seem significant, it is important to remember that solar power systems are a long-term investment. The upfront costs can often be offset by the savings accumulated over the system’s lifespan, making solar power an economically viable choice in the long run.
Return on Investment
Investing in solar power for your home offers attractive long-term returns. The return on investment (ROI) is calculated by considering the upfront costs of the solar power system compared to the savings on energy bills over its lifespan.
The precise ROI of a solar power system varies depending on factors such as geographical location, energy consumption, local energy prices, and the availability of government incentives or rebates. However, it is common for solar power systems to provide a return on investment within a span of five to ten years.
After recovering the initial investment, the savings from reduced energy costs can add up significantly over the remainder of the solar power system’s lifespan. Solar panels typically have a warranty of 25 to 30 years, ensuring continued energy savings well into the future.
Long-Term Savings
One of the key attractions of solar power for homes is the long-term savings it offers. By generating your electricity, you can substantially lower your energy bills over time. As energy prices continue to rise, your solar power system locks in your electricity costs, shielding you from future hikes in utility rates.
The exact amount of savings depends on factors such as the size of your solar power system, the amount of sunlight available in your location, and your energy consumption patterns. However, homeowners can typically expect to save thousands of dollars over the lifespan of their solar power system.
In addition to reduced energy costs, solar power also adds value to your home. Properties equipped with solar panels are highly sought after in the real estate market, often commanding higher selling prices and attracting potential buyers who value sustainability and energy efficiency.
Maintenance and Upkeep
Regular Cleaning and Inspection
While solar power systems require minimal maintenance, regular cleaning and inspection are necessary to ensure optimal performance. Dust, dirt, and debris can accumulate on the surface of the solar panels, reducing their efficiency and energy production.
Cleaning the solar panels with a soft brush or sponge and mild soap can help remove any accumulated grime. It is important to avoid abrasive materials that could scratch the surface of the panels. Regular cleaning should be performed at least twice a year, or more frequently in regions with heavy pollution or dust.
In addition to cleaning, regular inspections of the solar panels, inverters, batteries, and charge controllers are recommended. Inspecting for any visible damage, loose connections, or signs of wear and tear can help identify and address issues before they escalate. If you are unsure about performing inspections yourself, it is advisable to hire a professional solar technician to conduct routine maintenance.
Monitoring Energy Production
Monitoring the energy production of your solar power system is essential to ensure optimal performance and identify any potential issues. Many solar inverters come equipped with monitoring systems that allow you to track the electricity output of your solar panels.
By regularly checking the energy production levels, you can detect any significant variations or drops in output, indicating a possible problem with the system. Monitoring systems may also provide valuable data for analyzing energy consumption patterns, which can help you make informed decisions about energy usage and efficiency.
Replacing Components
While solar power systems are designed to be durable and long-lasting, certain components may need replacement over time. The lifespan of solar panels, for instance, typically ranges from 25 to 30 years. Inverters may have a shorter lifespan, averaging around 10 to 15 years. Battery storage systems may also require replacement after several years, depending on their lifespan and usage.
Regular maintenance and inspections can help identify components that may be nearing the end of their lifespan. Planning for component replacements in advance allows you to budget for the necessary expenses and ensures the continued efficiency and functionality of your solar power system.

This image is property of images.unsplash.com.
Backup Power Options
Connecting to the Grid
Connecting your solar power system to the grid provides a reliable backup power option. During periods of high energy demand or when your solar panels are not generating sufficient electricity, you can draw power from the grid to meet your needs. This is especially useful during nighttime or extended periods of cloudy weather.
Grid-connected solar power systems often have the ability to sell excess energy back to the grid, earning you credits or monetary compensation. This arrangement, known as net metering or feed-in tariffs, can further reduce your energy costs and provide additional financial benefits.
Using Backup Generators
In situations where grid connection is not available or during extended power outages, backup generators can provide an alternative source of electricity. Backup generators can be powered by various fuels, including gasoline, propane, or natural gas, ensuring a continuous supply of electricity even when sunlight is limited.
It is important to note that backup generators are typically not designed to power your entire home continuously. They are best suited for critical systems, such as refrigeration, lighting, and essential electronics, during emergency situations. Proper maintenance and regular testing of backup generators are essential to ensure their reliability when needed.
Choosing the Right Backup System
When considering backup power options for your solar power system, it is crucial to select the most suitable solution for your needs. Evaluate factors such as the frequency and duration of power outages in your area, the critical systems you wish to power during emergencies, and your budget.
While grid connection provides backup power and the ability to sell excess energy, it may not be available in all locations. Backup generators offer reliable power during extended outages but require fuel and regular maintenance. Assessing your specific requirements will help you determine the backup system that ensures uninterrupted electricity supply for your home.
Solar Power Limitations
Weather Dependency
One of the inherent limitations of solar power is its dependence on weather conditions. Solar panels generate electricity from sunlight, meaning that they are most productive during bright, sunny days. Cloud cover, fog, or rain can significantly reduce the energy output of solar panels.
However, advancements in solar technology, such as the development of more efficient panels and the integration of battery storage, have mitigated the impact of weather dependency. Battery storage systems allow the excess energy generated during peak sunlight hours to be stored for use during periods of low sunlight or at night, ensuring a consistent power supply.
Limited Energy Storage
While battery storage systems provide a solution for storing excess energy, they have limited capacity. Battery storage can only store a certain amount of energy, which means that if electricity demands exceed the stored energy, backup power sources might be required.
The size of the battery storage system needs to be carefully determined based on your energy requirements and desired level of energy independence. Properly sizing the battery storage ensures that there is adequate stored energy available during periods of low sunlight, minimizing the need for external backup power sources.
High Initial Investment
One of the primary limitations of solar power for homes is the initial investment required for installing a solar power system. The upfront costs associated with purchasing and installing solar panels, inverters, battery storage, and additional components can be substantial.
However, it is important to note that the long-term savings and financial benefits can outweigh the initial investment. With various government incentives and rebates available, as well as the potential for selling excess energy back to the grid, the return on investment can make solar power a financially viable choice in the long run.
Government Incentives and Rebates
Federal and State Incentive Programs
Governments at both the federal and state levels offer various incentives and rebates to encourage the adoption of solar power. These incentives aim to reduce the financial burden associated with installing solar power systems and promote the use of renewable energy sources.
Federal incentives may include investment tax credits, which allow homeowners to deduct a portion of their solar power system’s costs from their federal income taxes. State-level incentives can vary widely and may include grants, loan programs, property tax exemptions, or sales tax exemptions.
To take advantage of these incentive programs, it is important to research the offerings specific to your location and consult with a professional installer who is knowledgeable about the available incentives. They can guide you through the process of applying for and utilizing these government programs.
Tax Credits and Rebates
In addition to government incentives, many utility companies and energy providers offer their own tax credits and rebates to customers who install solar power systems. These incentives can further lower the upfront costs associated with going solar, making it a more attractive and affordable option for homeowners.
Contacting your local utility company or visiting their website can provide valuable information about any available rebates or credits. These incentives, combined with government programs, can significantly reduce the overall investment required for installing a solar power system.
Is Running a House Completely on Solar Power Realistic?
Factors to Consider
Running a house completely on solar power is a realistic possibility for many homeowners, depending on various factors. The viability of relying solely on solar power depends on aspects such as energy consumption patterns, geographical location, available sunlight, and the size of the solar power system.
To determine the feasibility of running a house completely on solar power, evaluate your energy needs and consumption habits. Consider the efficiency of your appliances and electronics, and look for opportunities to reduce your energy consumption through energy-efficient practices.
Suitability for Different Situations
The suitability of running a house completely on solar power can vary depending on individual circumstances. In regions with abundant sunshine and favorable solar potential, solar power can provide a substantial portion of a home’s energy needs or even cover the entire energy consumption.
In areas with less sunlight or high energy demands, running a house completely on solar power might require a larger solar power system, additional battery storage, or alternative backup power options. Each situation is unique, and it is important to assess your specific circumstances to determine the most realistic and efficient approach.
Tips for Transitioning to Solar Power
Transitioning to solar power for your home is an exciting and eco-friendly choice. To ensure a smooth and successful transition, consider the following tips:
- Research reputable solar installers and obtain multiple quotes: Compare quotes from different installers to ensure you receive competitive pricing and quality service.
- Educate yourself about government incentives and rebates: Take advantage of available government programs to maximize your financial benefits.
- Analyze your energy consumption and look for energy-efficient practices: Reduce your energy consumption by implementing energy-saving measures, such as using energy-efficient appliances, optimizing lighting, and adopting smart energy management practices.
- Seek professional advice on system sizing and placement: Consult with a professional solar installer to accurately size your solar power system and optimize its placement for maximum efficiency.
- Regularly maintain and monitor your solar power system: Keep your system in optimal condition by performing routine cleaning, inspections, and maintenance. Monitor energy production to identify any potential issues promptly.
By following these tips and utilizing the expertise of professionals, you can successfully transition to solar power and enjoy the benefits of clean, renewable energy for your home.
In conclusion, the advantages of solar power for homes are numerous and compelling. From reduced energy costs and environmental benefits to energy independence, solar power offers homeowners an opportunity to embrace sustainability while enjoying financial savings. Understanding the components of a solar power system, optimizing installation and placement, accurately sizing the system, and considering backup power options are key factors in maximizing the benefits of solar power for your home. While there are limitations and upfront costs associated with installing a solar power system, the long-term savings, return on investment, and various government incentives make solar power a realistic and desirable choice for homeowners. Transitioning to solar power requires careful consideration of individual circumstances and energy needs, but with proper planning and professional assistance, running a house completely on solar power becomes an achievable and rewarding endeavor.